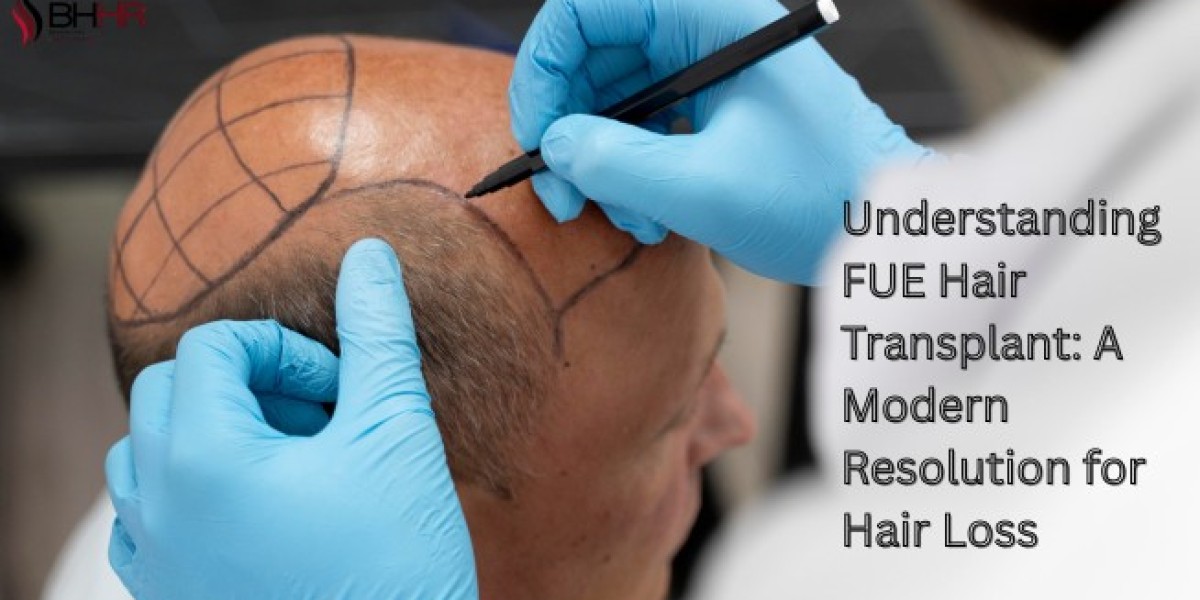
Hair loss is something millions of people face around the world. Whether it's caused by genetics, the natural ageing process, or certain health conditions, it can take a real toll on your self-confidence and how you feel about yourself. The good news? Thanks to improvements in medical science, there are now effective ways to bring back a fuller, more natural-looking head of hair. One of the most popular options today is the FUE hair transplant—a modern, minimally invasive procedure that helps people regain not just their hair, but also their confidence.
What is an FUE Hair Transplant?
FUE is the acronym for Follicular Unit Extraction. In this method, single hair follicles are extracted from the donor region (generally the back or sides of the head) and transplanted to the balding or thinning regions. Unlike the older methods, where a strip of scalp was removed, the FUE hair transplant does not cause a linear scar and has minimal recovery time. Each follicle is pulled out with a specially designed micro punch tool measuring approximately 0.7 to 1 millimetre in diameter. This allows a natural-looking hairline and coverage, so there is a smooth blend with your current hair.
Why Choose FUE Over Other Hair Restoration Methods?
The FUE hair transplant method offers several advantages over traditional techniques, such as FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation). These benefits include:
Minimally invasive: No stitches or scalpel required
Faster recovery: Most patients continue normal activities within a few days
Minimal scarring: Only tiny, dot-like scars that are barely noticeable
Natural results: Hair grows in naturally, following the direction and pattern of existing hair
Due to these advantages, many patients prefer FUE hair transplant as their first choice for hair restoration.
Ideal Candidates for FUE Hair Transplant
While FUE hair transplant is effective, not everyone may be a suitable candidate. The ideal candidate usually:
Has moderate hair loss with enough donor hair available
Is in good overall health
Has realistic expectations
Is experiencing pattern baldness or thinning due to age or genetics
Individuals with extensive hair loss or medical conditions that affect hair growth may need to consult a specialist to determine the best course of action.
The Procedure: What to Expect
The FUE hair transplant procedure typically begins with a consultation to evaluate hair loss patterns and discuss expectations. On the day of the treatment, the scalp is cleaned and numbed with local anaesthesia. Then, individual follicles are extracted from the donor area and prepared for implantation. The surgeon produces tiny incisions in the recipient site and strategically places the hair follicles to mimic natural growth. The process can take 4 to 8 hr, depending on the number of hair grafts you need. It’s a detailed process, but most patients find it manageable and well worth the time for the long-lasting results. One of the most trusted clinics offering this advanced procedure is Beverly Hills Hair Restoration. Known for its talented team and personalised approach, the clinic has helped thousands achieve natural-looking results with FUE hair transplant techniques.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovering from an FUE hair transplant is usually pretty easy and straightforward. You might catch some mild swelling, redness, or tiny scabs where the hair was transplanted, but these usually go away in a few days. Just be sure to follow your doctor’s aftercare instructions—that’s the best way to heal properly and help your new hair grow in strong and healthy.
Key aftercare tips include:
Avoid touching or scratching the treated areas
Refrain from strenuous activities for a few days
Use mild shampoos and avoid harsh hair products
Protect the scalp from direct sunlight
New hair development typically begins within 3 to 4 months, with full marks visible in 9 to 12 months.
Results That Last
One of the best things about an FUE hair transplant is how long the results last. The hair that's transplanted comes from areas resistant to DHT—the hormone that causes most hair loss—so it keeps growing naturally for years. With the right care, the results can even last a lifetime. Many patients at Beverly Hills Hair Restoration say they’re thrilled with the outcome, often mentioning how much better they feel about their appearance and confidence. The clinic’s focus on cutting-edge techniques and top-notch patient care really sets it apart in the world of hair restoration.
Cost Considerations
The cost of an FUE hair transplant can vary based on several factors, including:
Number of grafts needed
Surgeon’s expertise
Clinic location
Additional services and follow-ups
While the initial acquisition may seem high, the long-term benefits of restored hair and confidence make it worthwhile for many. Choosing a reputable clinic like Beverly Hills Hair Restoration ensures you get quality treatment with excellent value for money.
Why Choose Beverly Hills Hair Restoration?
Many clinics are offering FUE hair transplant services, but not all deliver the same level of excellence. Beverly Hills Hair Restoration stands out due to its:
Board-certified hair transplant surgeons
Cutting-edge equipment and facilities
Customised treatment plans
Proven way to record with thousands of successful procedures
Conclusion
Hair loss doesn’t have to be something you just live with anymore. With FUE hair transplants, there’s now a safe and simple way to bring back your hair—and your confidence. Whether your hair has just started thinning or you've been dealing with hair loss for a while, this procedure offers a modern solution that really works. If you're thinking about getting an FUE transplant, it’s important to choose a trusted clinic like Beverly Hills Hair Restoration. Their team will guide you through the process and help you get the natural-looking results you want. Book a consultation and take the first step toward feeling like yourself again.