Autoimmune diseases have long posed a challenge for patients and healthcare providers. Traditional treatments often come with significant side effects and limited effectiveness. However, the rise of Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors has revolutionized the way we manage autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, ulcerative colitis, and alopecia areata. These cutting-edge drugs are changing lives by offering targeted, more effective, and often more convenient treatment options.
What Makes JAK Inhibitors a Game-Changer?
JAK inhibitors work by blocking specific enzymes (Janus kinases) involved in immune system signaling. By doing so, they help reduce inflammation and immune system overactivity, which are the root causes of many autoimmune diseases. Unlike traditional immunosuppressants that broadly suppress the immune system, JAK inhibitors offer a more precise approach, reducing the risk of widespread immune suppression.
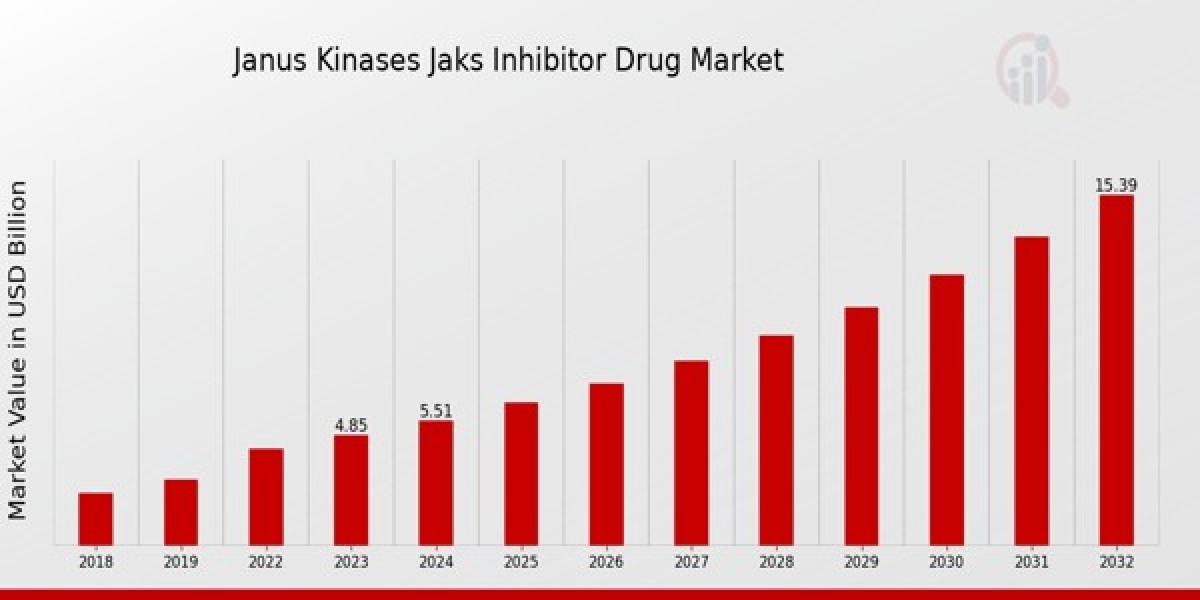
Janus Kinases JAKs Inhibitor Drug Market Overview
As per MRFR analysis, the Janus Kinases JAKs Inhibitor Drug Market Size was estimated at 6.27 (USD Billion) in 2024. The Janus Kinases JAKs Inhibitor Drug Market Industry is expected to grow from 7.12 (USD Billion) in 2025 to 22.66 (USD Billion) till 2034, at a CAGR (growth rate) is expected to be around 13.72% during the forecast period (2025 - 2034).
JAK Inhibitors in Action: Which Diseases Do They Treat?
JAK inhibitors have shown promising results in treating a variety of chronic autoimmune diseases, including:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) – Patients who fail to respond to conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) now have JAK inhibitors like Tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and Baricitinib (Olumiant) as effective alternatives.
- Psoriatic Arthritis – These drugs help manage joint inflammation and skin symptoms, offering relief to many patients.
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) – Conditions like ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are now being managed with JAK inhibitors such as Upadacitinib (Rinvoq).
- Alopecia Areata – The recent FDA approval of Baricitinib for alopecia areata has brought hope to those suffering from severe hair loss due to autoimmunity.
- Atopic Dermatitis – JAK inhibitors have emerged as an effective treatment for severe eczema, offering relief to patients who do not respond to topical treatments.
Oral vs. Injectable: A Treatment Shift
One of the biggest advantages of JAK inhibitors is their oral formulation. Unlike biologic drugs, which are typically administered via injections, many JAK inhibitors are taken as oral pills. This shift has made treatment more convenient and has improved patient compliance, as many individuals prefer pills over injections.
Are There Any Risks?
Despite their benefits, JAK inhibitors are not without risks. Some potential side effects include:
- Increased risk of infections due to immune modulation
- Blood clots and cardiovascular risks in certain patients
- Potential liver and kidney function changes
Due to these risks, healthcare providers carefully evaluate patients before prescribing JAK inhibitors and often conduct regular blood monitoring during treatment.
The Future of JAK Inhibitors in Medicine
As research continues, new generations of JAK inhibitors with improved safety profiles and enhanced specificity are expected to emerge. Scientists are also exploring their potential use in treating conditions like lupus, multiple sclerosis, and even certain types of cancers.
The advent of JAK inhibitors marks a new era in autoimmune disease treatment, offering hope to millions of patients worldwide. As innovations continue, we can expect even greater advancements in personalized and targeted therapies, making autoimmune diseases more manageable than ever before.
For more information, please visit @marketresearchfuture