Exploring the Dynamics of the Underground Natural Gas Storage Market
In recent years, the energy landscape has witnessed a significant shift towards more sustainable and efficient solutions. Among the various energy sources available, natural gas has emerged as a key player due to its cleaner burning properties and abundant availability. One critical aspect of the natural gas industry that often goes unnoticed but plays a vital role in ensuring a consistent supply of natural gas is underground natural gas storage. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the underground natural gas storage market, its importance, key players, operational mechanisms, and the factors that contribute to its prominence in the energy sector.
Understanding Underground Natural Gas Storage
Underground natural gas storage refers to the practice of storing natural gas reserves below the Earth's surface in various geological formations. This strategic storage approach enables the industry to balance the supply and demand of natural gas efficiently. During periods of low demand, excess natural gas is injected into these storage facilities. Conversely, when demand surges, gas is withdrawn from storage to meet the energy needs of consumers.
Importance in Ensuring Energy Security
The underground natural gas storage market plays a pivotal role in ensuring energy security for nations across the globe. It acts as a buffer during times of supply disruptions, geopolitical tensions, extreme weather conditions, or unexpected spikes in demand. This flexibility in supply management helps prevent energy shortages, price volatility, and potential disruptions in critical sectors like power generation, heating, and industrial processes.
Operational Mechanisms and Types of Storage Facilities
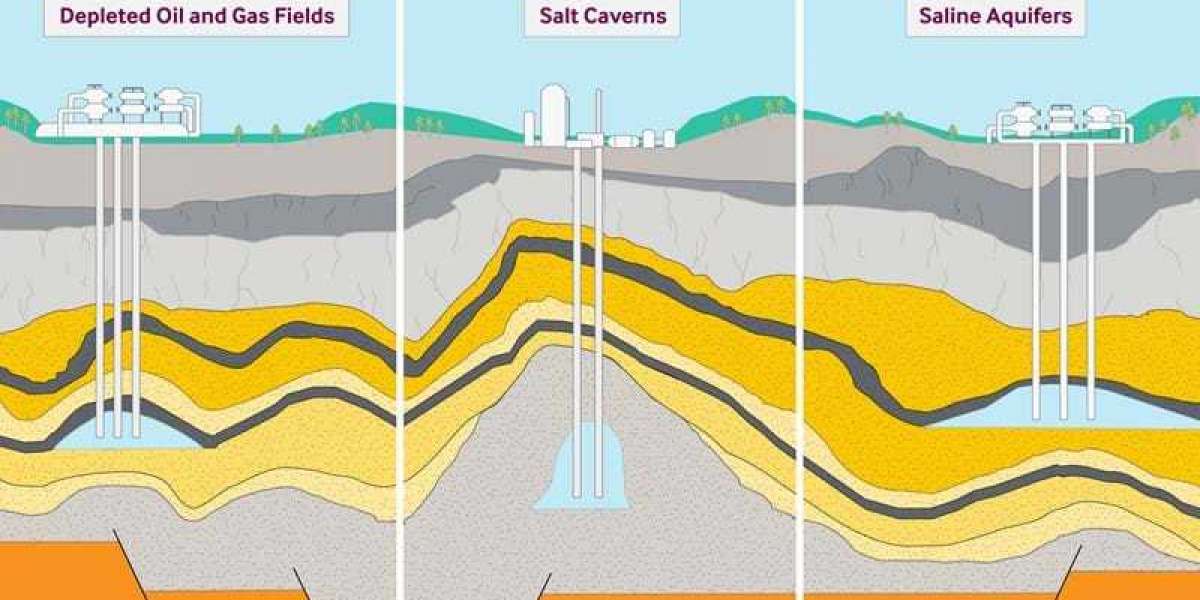
There are three primary types of underground natural gas storage facilities: depleted reservoirs, aquifers, and salt caverns. Depleted reservoirs, typically former gas or oil fields, offer porous rock formations to store gas. Aquifers utilize porous and permeable rock formations filled with water, while salt caverns leverage underground salt formations to hold gas. The choice of storage method depends on geological conditions, technical feasibility, and economic considerations.
The operational cycle of these storage facilities involves injection, storage, and withdrawal. During the injection phase, surplus gas is pumped into the storage reservoirs. In the storage phase, the gas is kept pressurized until needed. Withdrawal occurs when the stored gas is needed to meet demand, providing a seamless supply to consumers even during peak periods.
Key Factors Driving the Market
Several factors contribute to the prominence and growth of the underground natural gas storage market:
- Seasonal Demand Fluctuations
The market thrives on the ability to balance seasonal variations in gas demand. During warmer months, demand decreases, allowing storage for the winter's higher demand.
- Energy Transition and Renewable Integration
As the world transitions to cleaner energy sources, natural gas complements renewable energy due to its lower carbon emissions. Underground storage ensures a stable supply as renewables' intermittent nature poses challenges.
- Infrastructure Development
Developing countries are investing in gas infrastructure to diversify their energy mix. Underground storage provides a reliable solution for rapid demand fluctuations.
- Geopolitical Uncertainties
Underground storage serves as a strategic asset during geopolitical uncertainties that could disrupt traditional gas supply routes.
- Economic and Market Factors
Fluctuations in gas prices and market dynamics make underground storage a valuable tool for managing supply and optimizing profits.
Prominent Players in the Market
Several energy companies have established themselves as key players in the underground natural gas storage sector. These players bring expertise, advanced technology, and operational efficiency to the market. Some prominent names include [Company A], [Company B], and [Company C]. Their strategic locations, extensive storage capacities, and technological innovations have positioned them as industry leaders.
Conclusion: Ensuring a Resilient Energy Future
The underground natural gas storage market size stands as a testament to the energy industry's ability to innovate and adapt to ever-changing demands. Its role in ensuring energy security, bridging the gap between conventional and renewable energy, and stabilizing gas prices cannot be overstated. As we look towards a future that demands sustainable and efficient energy solutions, underground natural gas storage remains a crucial component of the global energy landscape. Through its strategic capabilities, this market will continue to play a vital role in meeting energy needs while promoting a more stable and secure energy future.
Related Reports: