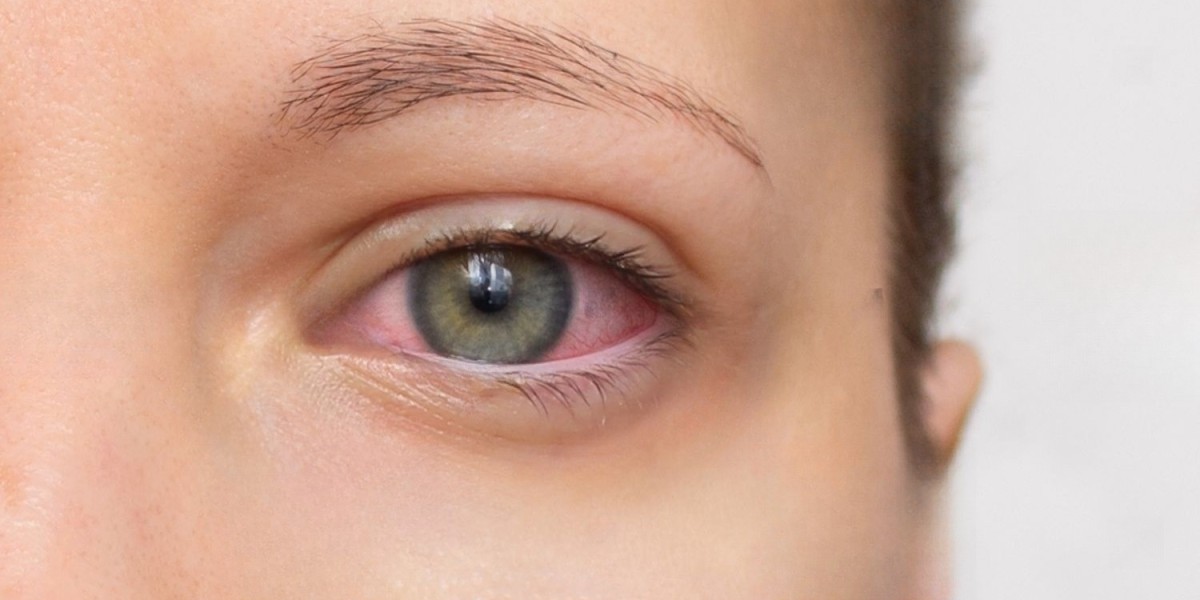
Uveitis – inflammation of the eye's middle layer – can silently threaten your vision if left untreated. Recognizing Uveitis Symptoms early is crucial to prevent permanent damage.
This essential guide reveals:
✔ What uveitis is and why it’s dangerous
✔ The 10 critical Uveitis Symptoms demanding attention
✔ How symptoms differ by uveitis type
✔ When to seek emergency care
✔ Modern treatment options
Don’t risk your eyesight – learn to spot these warning signs today.
What Is Uveitis?
Uveitis targets the uvea (iris, ciliary body, and choroid), but can affect all eye structures. Causes include:
Autoimmune disorders (RA, lupus)
Infections (herpes, tuberculosis)
Eye injuries
Unknown causes (idiopathic)
"30% of uveitis patients suffer permanent vision loss – mostly from delayed diagnosis." – American Academy of Ophthalmology
10 Critical Uveitis Symptoms
1. Eye Redness That Won’t Fade
What’s abnormal: Sectoral redness (one section) or whole-eye inflammation
Unlike: General pink eye that improves in days
2. Throbbing Eye Pain
Feels like: Deep ache behind the eye
Worsens with: Eye movement or bright light
3. Sudden Light Sensitivity
Key sign: Discomfort from normal indoor lighting
Indicates: Active intraocular inflammation
4. Blurred or Cloudy Vision
Pattern: Fluctuates throughout the day
Danger sign: "Floaters" increasing suddenly
5. Floating Spots in Vision
Appearance: Cobwebs or dark specks
Emergency: Sudden "floaters shower" (retinal tear risk)
6. Small or Irregular Pupil
Medical term: Posterior synechiae
Seen in: Iritis (anterior uveitis)
7. Headaches with Eye Discomfort
Location: Brow ache or temple pain
Red flag: Worse upon waking
8. Reduced Night Vision
Early sign: Difficulty adjusting to darkness
Mechanism: Retinal inflammation
9. Unusual Tearing
Notable: Only one eye waters excessively
Timing: Persistent for days
10. Vision Loss (Late Stage)
Progression: Gradual or sudden
Causes: Glaucoma, cataracts, or macular edema
Symptoms by Uveitis Type
| Type | Location | Hallmark Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Anterior | Front eye | Pain, photophobia, redness |
| Intermediate | Vitreous | Floaters, blurred vision |
| Posterior | Retina/choroid | Vision loss, night blindness |
| Panuveitis | All layers | Combined severe symptoms |
When to Seek Emergency Care
Go immediately if you experience:
? Sudden vision loss
? Severe pain with nausea
? White pupil (hypopyon)
? Flashes with floaters
"24-hour delay in treatment can mean permanent vision loss in posterior uveitis." – Dr. Susan Lightman, Uveitis Specialist
Diagnosis: What to Expect
Slit-lamp exam (microscopic eye evaluation)
OCT scan (retinal thickness measurement)
Blood tests (for systemic causes)
Fluorescein angiography (vascular imaging)
Modern Treatment Options
1. Medications
Steroid eye drops (for anterior uveitis)
Oral prednisone (moderate cases)
Immunosuppressants (methotrexate, biologics)
2. Surgical Interventions
Vitrectomy (for severe floaters)
Implantable steroid devices (chronic cases)
3. Emerging Therapies
JAK inhibitors (like tofacitinib)
Localized drug delivery systems
Long-Term Complications
Untreated uveitis risks:
Glaucoma (30% of chronic cases)
Cataracts (from prolonged steroids)
Macular edema (leading cause of vision loss)
Retinal detachment
Prevention & Monitoring
✔ Regular eye exams if autoimmune conditions exist
✔ UV-protective sunglasses for light sensitivity
✔ Immediate reporting of symptom recurrence
Final Warning
Uveitis Symptoms often masquerade as minor irritations – but this invisible inflammation can steal your sight. Don’t dismiss persistent eye changes.
FAQs About Uveitis Symptoms
Q: Can uveitis go away on its own?
A: Rarely – most cases require treatment to prevent complications.
Q: Is uveitis contagious?
A: No, unless caused by specific infections (like tuberculosis).
Q: How fast does treatment work?
A: Pain improves in 1-2 days; inflammation takes weeks to resolve.
Q: Can stress trigger uveitis?
A: Yes – stress worsens autoimmune-related flares.