Unlock the Secrets of Small Audio Mixers: Transform Your Sound Experience Today!
Small audio mixers are essential tools in today’s audio production landscape. With the rise of home studios, podcasts, and live-streaming events, these compact devices have become increasingly popular among musicians, content creators, and sound engineers. Their ability to blend multiple audio sources while maintaining quality makes them invaluable. In this article, we will delve into the various features of small audio mixers, explore their applications in different settings, and provide tips to help you choose the right one. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting out, understanding small audio mixers can significantly enhance your sound experience.
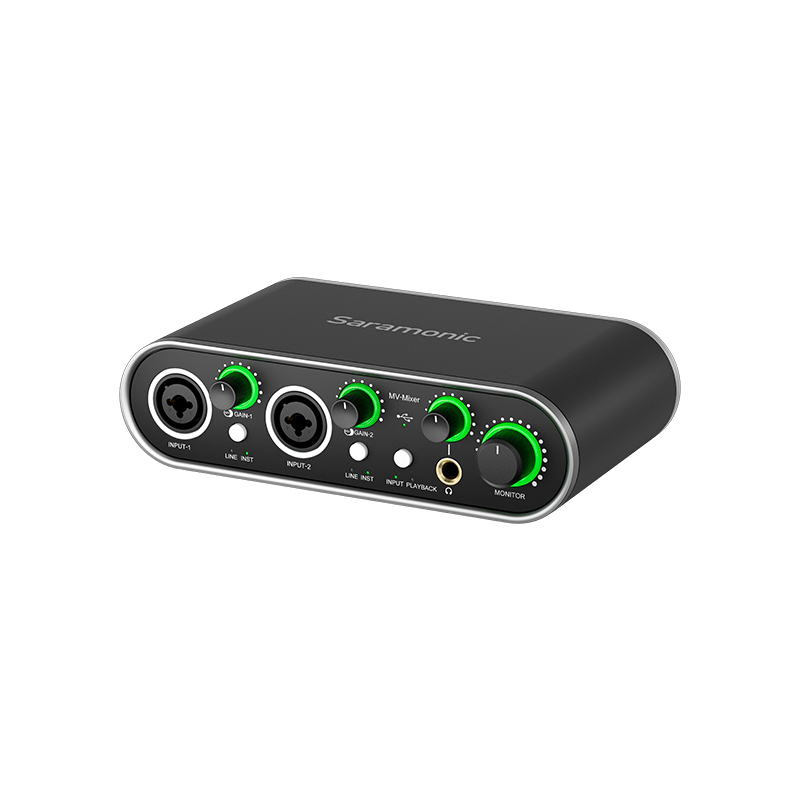

Understanding Small Audio Mixers
Small audio mixers are portable devices designed to combine multiple audio signals into one output. They are typically equipped with several input channels, allowing users to connect different sound sources, such as microphones, instruments, and playback devices. The primary functionality of a small audio mixer is to control the volume, tone, and effects of each input, ensuring a balanced final mix. There are various types of small audio mixers available, including analog and digital models. Analog mixers tend to be straightforward and user-friendly, making them suitable for live performances. In contrast, digital mixers offer advanced features such as built-in effects and multi-track recording capabilities, which are particularly beneficial in studio settings. Understanding the types and functionalities of small audio mixers is the first step toward optimizing your audio projects.
Key Features of Small Audio Mixers
The effectiveness of small audio mixers stems from their essential features. One of the most critical aspects is the number of input channels, which determines how many audio sources can be mixed simultaneously. Many mixers include EQ (equalization) controls, allowing users to adjust the bass, midrange, and treble frequencies for each channel, enhancing the overall sound quality. Furthermore, effects such as reverb, delay, and compression can be added to create depth and character in the audio. Connectivity options are also important; most small mixers offer USB interfaces for easy connection to computers, making them excellent for recording and live streaming. Additionally, some models provide headphone outputs for monitoring, ensuring that audio is mixed accurately. These features collectively enhance the user experience, making it easier to achieve professional-sounding results.
Applications in Various Audio Settings
Small audio mixers are versatile tools that can be applied in numerous audio settings. In home studios, they serve as the central hub for recording multiple instruments and vocals. By adjusting levels and applying effects in real-time, musicians can create polished tracks without needing extensive post-production. In live performance settings, small mixers allow sound engineers to manage audio levels for various performers, ensuring a clear and balanced sound for the audience. For instance, during a friend's band performance, I witnessed how a small mixer helped them adjust the vocals and instruments on-the-fly, resulting in a captivating show. In the realm of podcasting, small mixers can significantly enhance audio quality by enabling hosts to mix guest speakers, sound effects, and music seamlessly. Each of these applications highlights the importance of small audio mixers in producing high-quality sound across different contexts.
Tips for Choosing the Right Small Audio Mixer
Selecting the right small audio mixer can be a daunting task, given the variety of options available. Start by considering your budget, as prices can vary widely. Next, think about your intended use. Are you primarily recording music, hosting podcasts, or performing live? Understanding your needs will help narrow down your choices. Additionally, look for essential features that align with your requirements, such as the number of input channels, built-in effects, and connectivity options. If you're new to mixing, opting for a user-friendly model with intuitive controls can ease the learning curve. My friend, who recently started a podcast, found that a simpler mixer allowed him to focus more on content rather than technicalities, leading to a smoother recording process. Taking the time to assess your needs will ultimately lead you to the right small audio mixer.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While using small audio mixers can be straightforward, there are common pitfalls that users should be aware of. One frequent mistake is neglecting to properly set levels before mixing, which can lead to distorted sound. Always monitor the input levels to ensure they are within the optimal range. Another misconception is that more channels always mean better sound quality. In reality, understanding how to mix and balance audio is far more critical than simply having numerous inputs. Additionally, many users underestimate the importance of EQ settings; failing to adjust these can result in a muddy mix. Best practices include regularly experimenting with different settings, using reference tracks to compare sound, and continually learning about mixing techniques. By being aware of these issues and addressing them proactively, users can ensure that they achieve the best possible audio quality from their small audio mixers.
Summary of Small Audio Mixer Benefits
In summary, small audio mixers play a pivotal role in enhancing sound production across various settings. Their features, such as input channels, EQ controls, and connectivity options, make them indispensable for musicians, podcasters, and live performers alike. By understanding their functionality and applications, you can make informed decisions that elevate your audio projects. I encourage you to explore and experiment with small audio mixers to discover how they can transform your sound experience. Whether you're recording at home or performing live, the right mixer can make all the difference in achieving professional-quality audio.