Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS) is a rare but serious condition that affects identical twin pregnancies sharing a single placenta. This imbalance in blood flow between the twins can lead to severe complications, making early diagnosis and effective treatment crucial for better outcomes.
What is Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome?
TTTS occurs when the shared placenta causes an uneven distribution of blood supply between the twins. One twin, called the donor twin, receives less blood and nutrients, leading to slow growth and low amniotic fluid levels. The recipient twin, on the other hand, gets an excess supply, which can strain the heart and lead to complications like heart failure.
Causes and Risk Factors
TTTS happens due to abnormalities in the blood vessels within the placenta. Factors that may increase the risk include:
- Monochorionic twins: Identical twins that share a placenta are at higher risk.
- Abnormal vascular connections: Unequal distribution of placental blood vessels can lead to TTTS.
- Genetic factors: While TTTS is not inherited, certain placental issues may have genetic influences.
Signs and Symptoms
The condition can develop at any stage of pregnancy, and symptoms may include:
- Rapid growth of the mother’s belly due to excessive amniotic fluid in the recipient twin’s sac.
- Swelling and high blood pressure in the mother.
- Discrepancy in fetal size, with one twin appearing much smaller.
- Signs of heart failure in the recipient twin.
Diagnosis of TTTS
TTTS is typically diagnosed through ultrasound screenings, which assess:
- The levels of amniotic fluid in each twin’s sac.
- Differences in the twins’ sizes and weights.
- Blood flow patterns in the umbilical cord using Doppler ultrasound.
- Heart function in both twins.
Treatment Options for TTTS
The treatment plan for TTTS depends on its severity and the stage of pregnancy:
1. Expectant Management
For mild cases, close monitoring with frequent ultrasounds and maternal rest may be recommended to assess progression.
2. Amnioreduction
This procedure involves removing excess amniotic fluid from the recipient twin’s sac to relieve pressure and improve overall balance.
3. Fetoscopic Laser Surgery
The gold standard for severe TTTS, fetoscopic laser photocoagulation (FLP), seals off abnormal blood vessel connections in the placenta to restore equal blood flow. This minimally invasive surgery significantly improves survival rates.
4. Selective Reduction
In rare cases where one twin’s survival is at high risk, selective reduction may be considered to improve the other twin’s chances.
5. Early Delivery
If TTTS progresses later in pregnancy, doctors may recommend preterm delivery to ensure better neonatal care.
Outlook and Prognosis
The prognosis for TTTS varies based on the stage at diagnosis and the effectiveness of treatment. Advances in fetal surgery and neonatal care have significantly improved survival rates, but early detection remains key.
Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome Treatment Market Overview
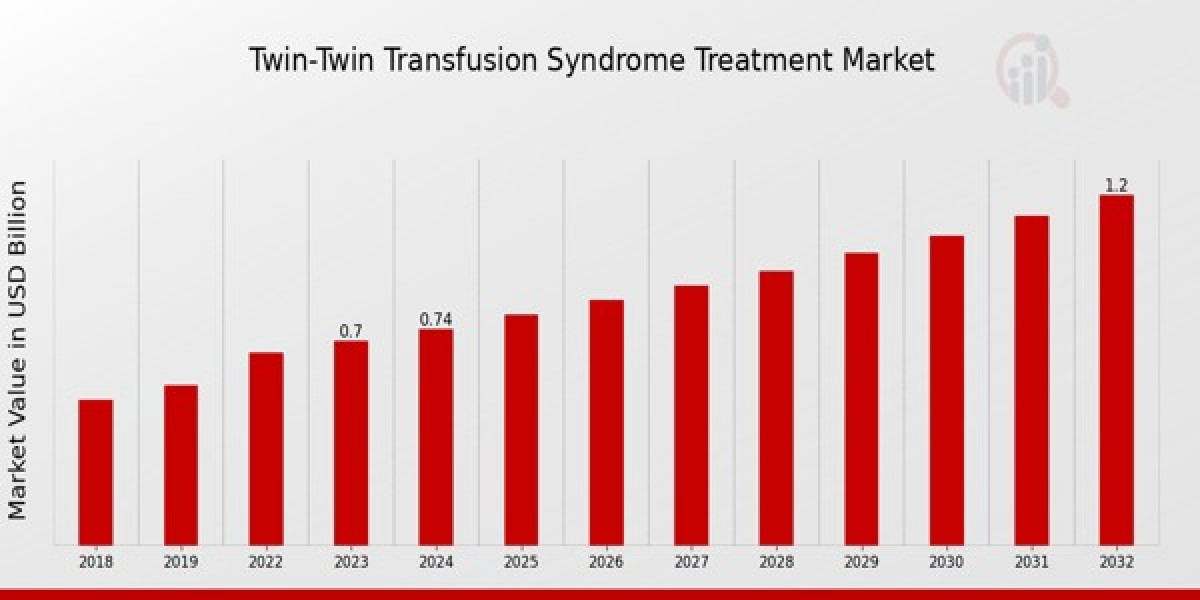
As per MRFR analysis, the Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome Treatment Market Size was estimated at 0.79 (USD Billion) in 2024. The Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome Treatment Market Industry is expected to grow from 0.84 (USD Billion) in 2025 to 1.44 (USD Billion) till 2034, at a CAGR (growth rate) is expected to be around 6.18% during the forecast period (2025 - 2034).
Final Thoughts
Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome is a complex condition requiring specialized care. Understanding the risks, symptoms, and available treatments can help expectant parents make informed decisions. With early intervention and advanced medical treatments like fetoscopic laser surgery, many TTTS-affected pregnancies result in successful outcomes.
For more information, please visit @marketresearchfuture